FesRobex Torque Joints Calculation
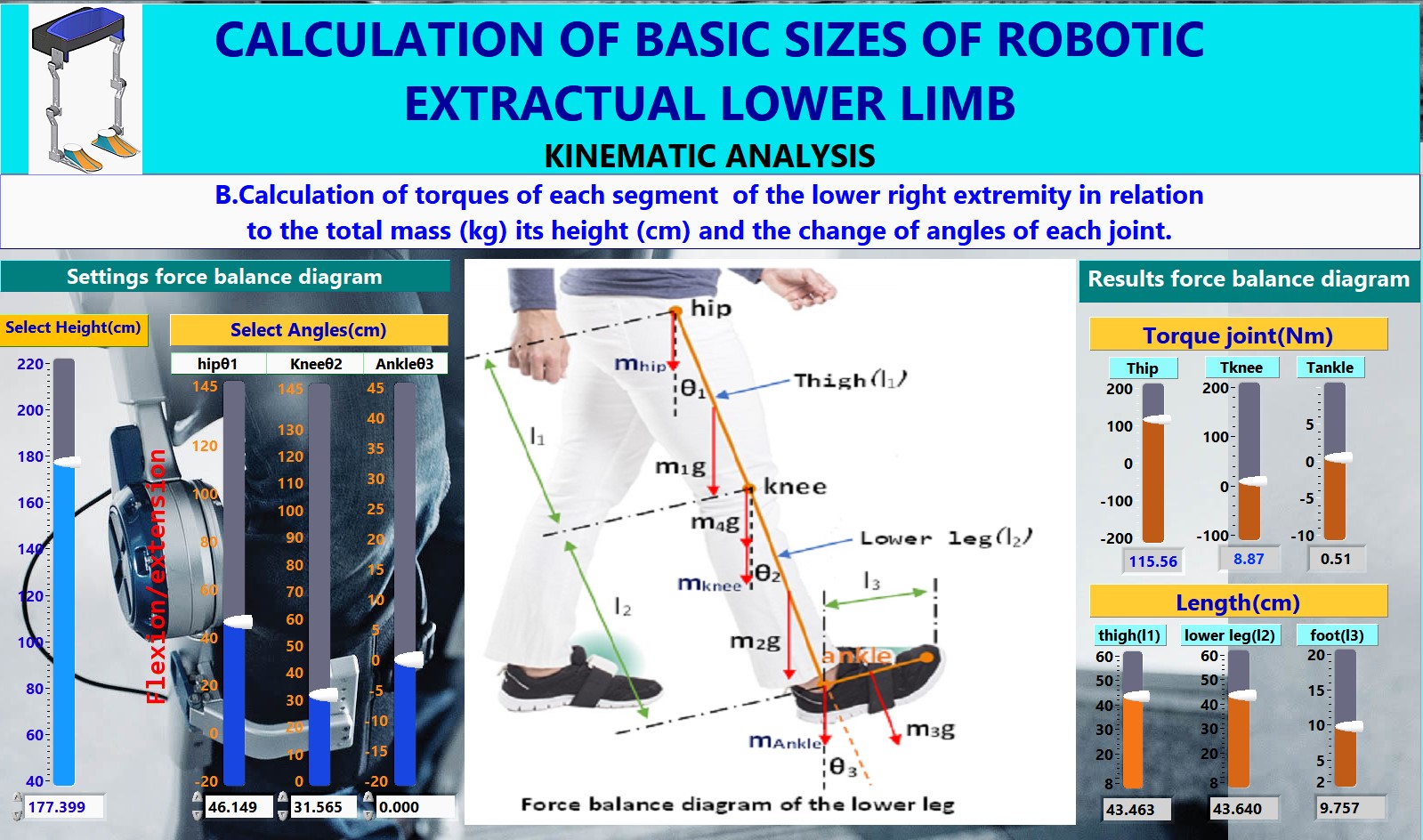
The mathematical model for calculating the torque of robotic exoskeleton joints using LabVIEW software. The calculation of torques is an important parameter for the correct choice of motors to achieve the torques we need in each joint of the robotic exoskeleton. In the mathematical model, there is the possibility of entering measurements of joint torques and characteristics for each servomotor in a SQL database and performing statistical analysis of servomotors. The aim is to make the right choice between brushed and brushless motors and to choose the right motor based on the torques developed on the joints of the FesRobex robotic exoskeleton (research model of an electric stimulation system of Fes hybrid function and Robex robotic exoskeleton). Healthcare 2022, 10(10), 2054; doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102054
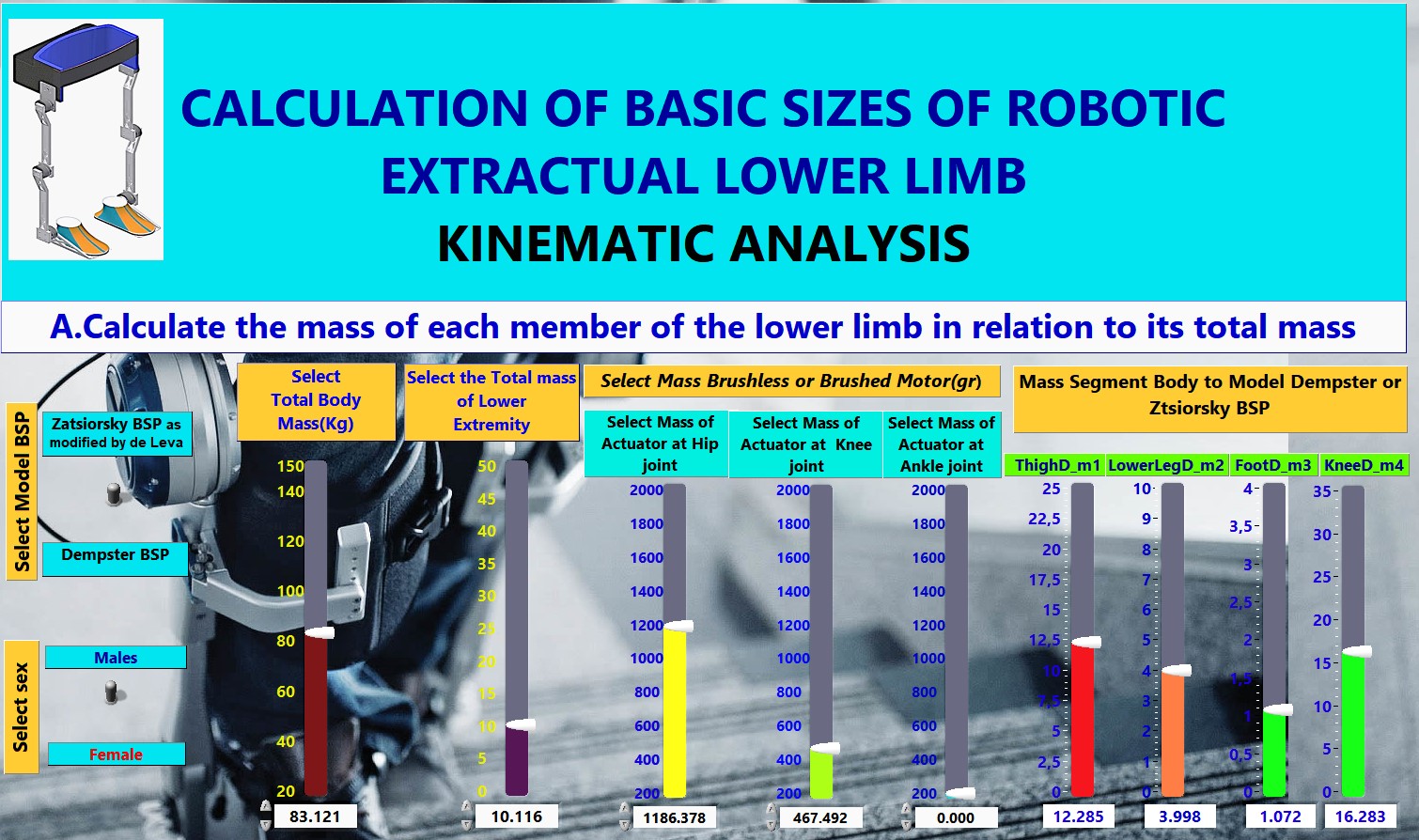
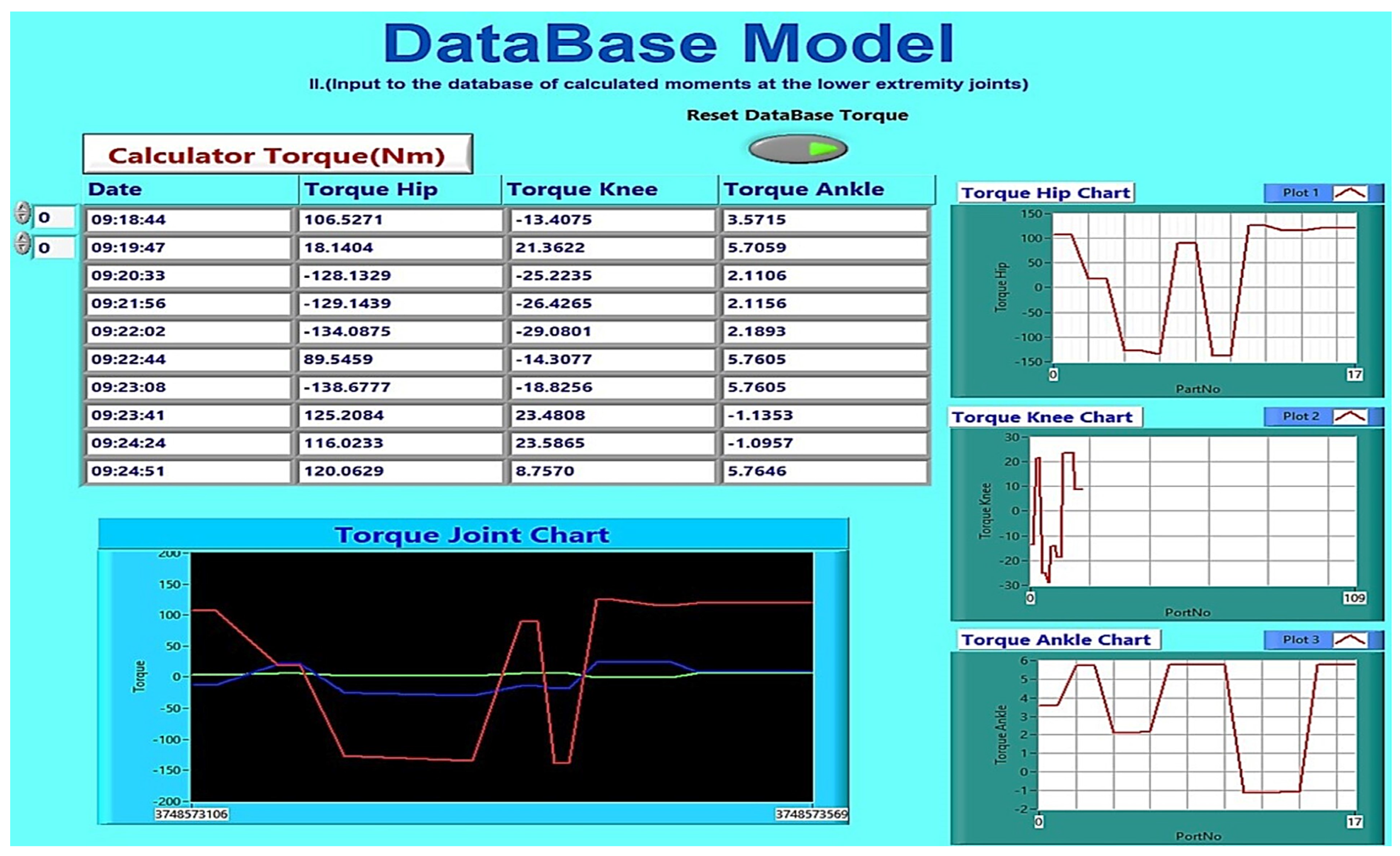
FesRobex Torque Joints Calculation GUI
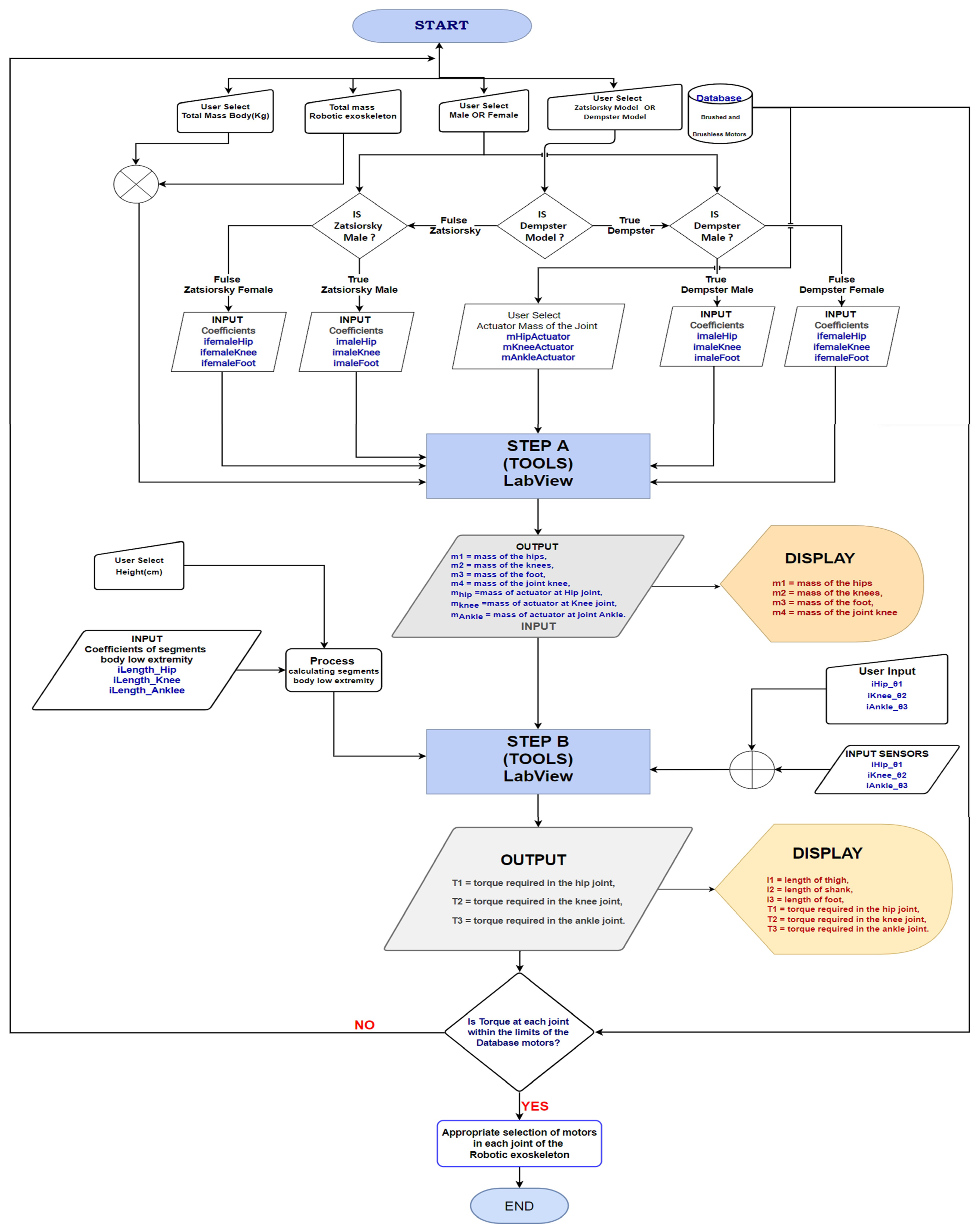
Flow chart Model
Force balance diagram of the lower leg
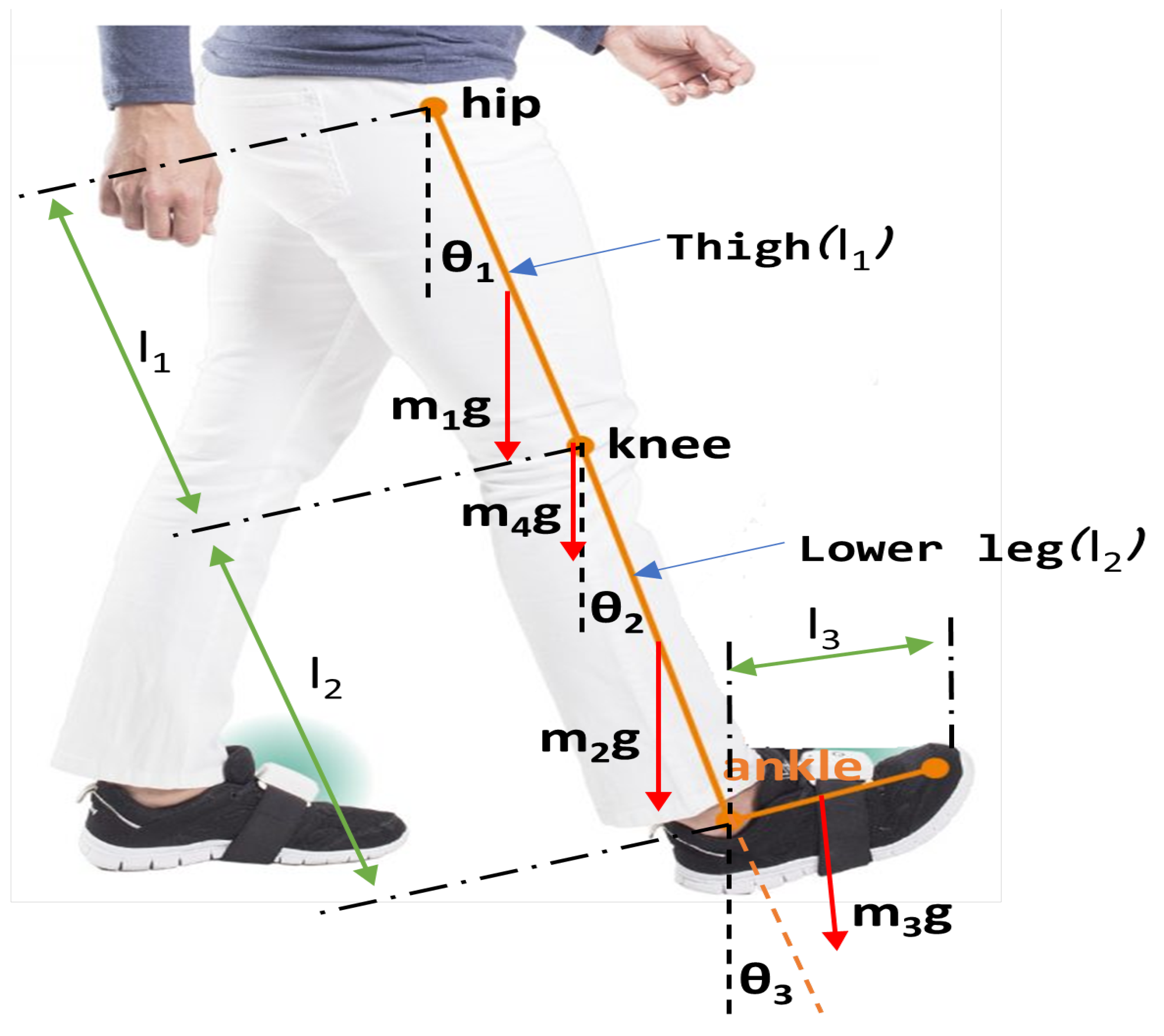
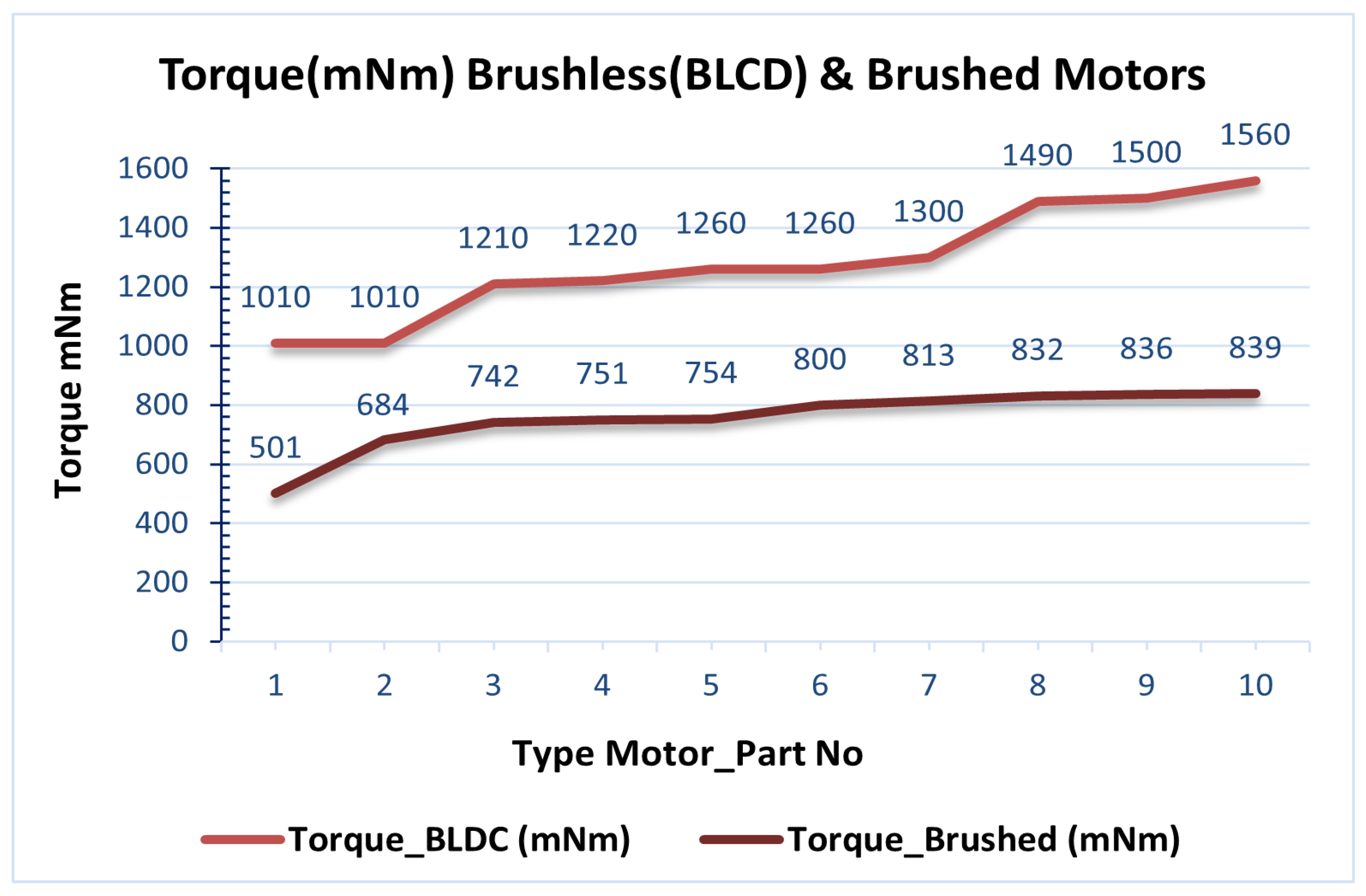
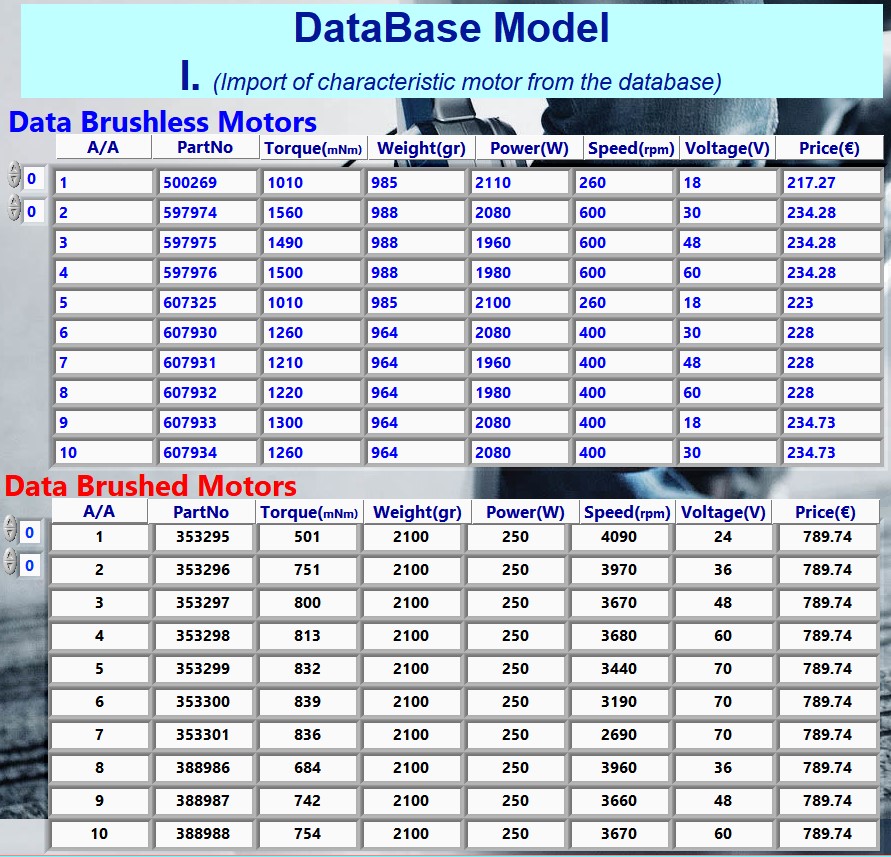
Table7.Comparison Quantitative Characteristics: Brushless (BLDC) and Brushed Motors
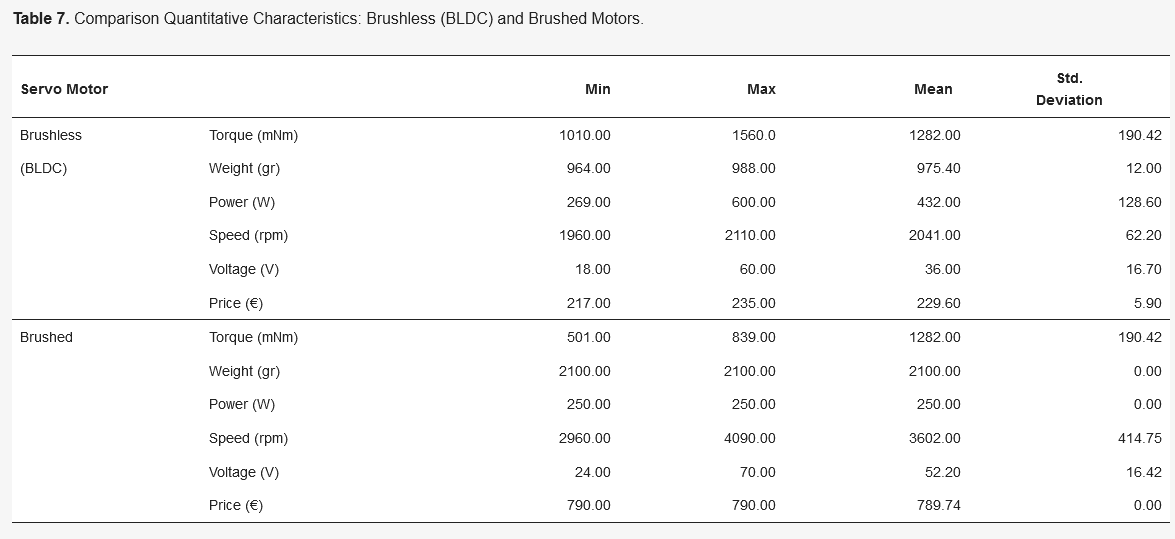
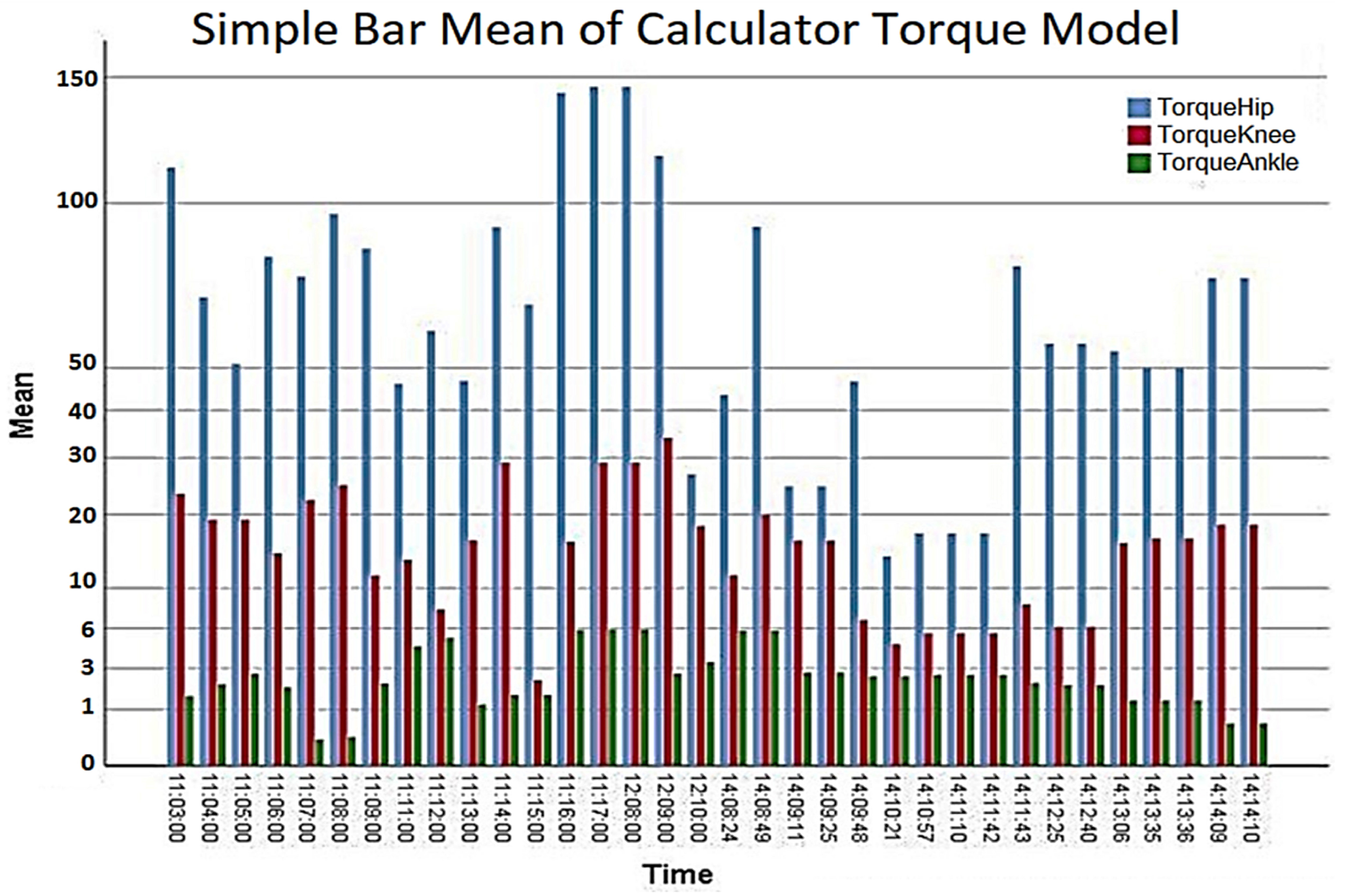
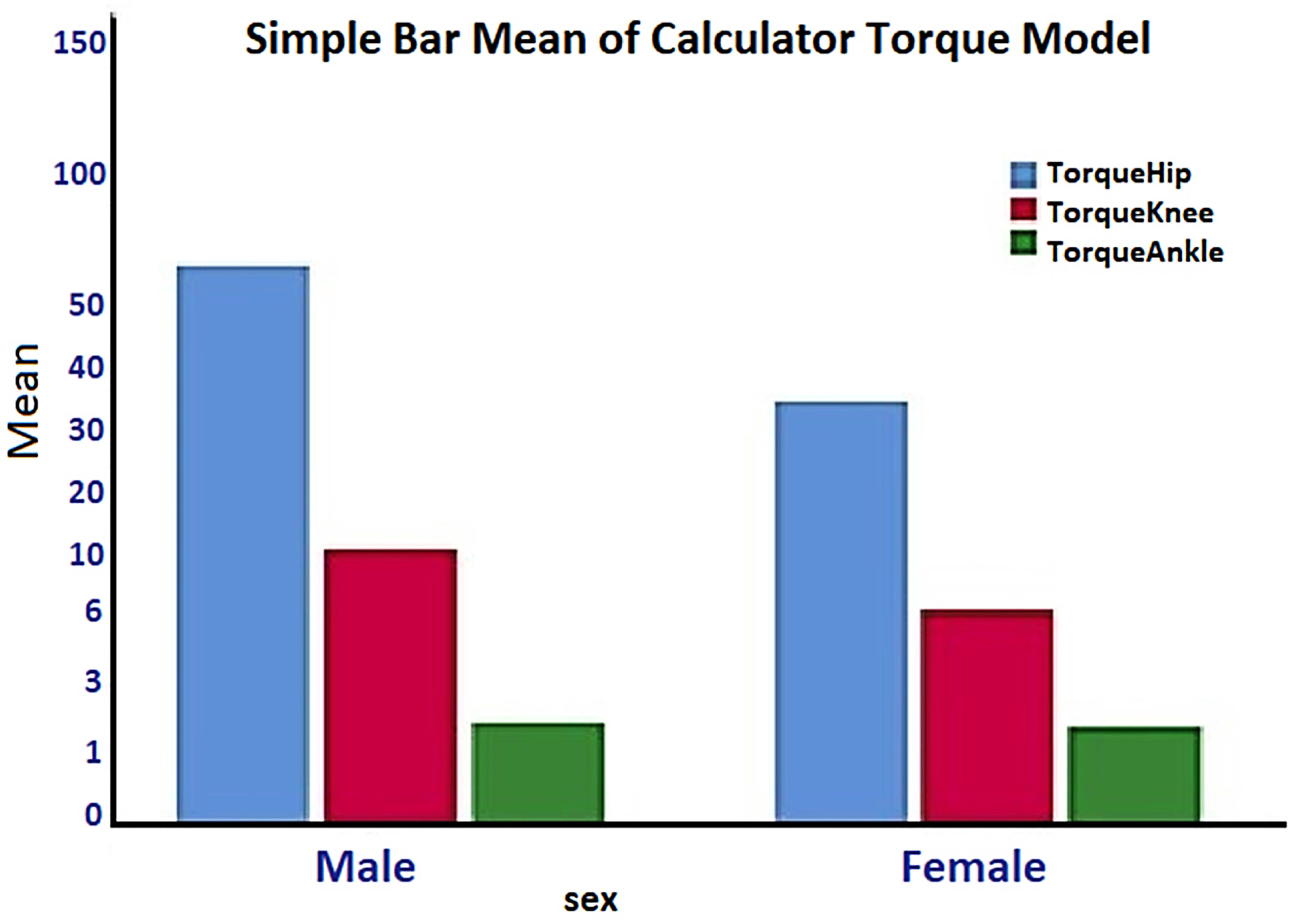
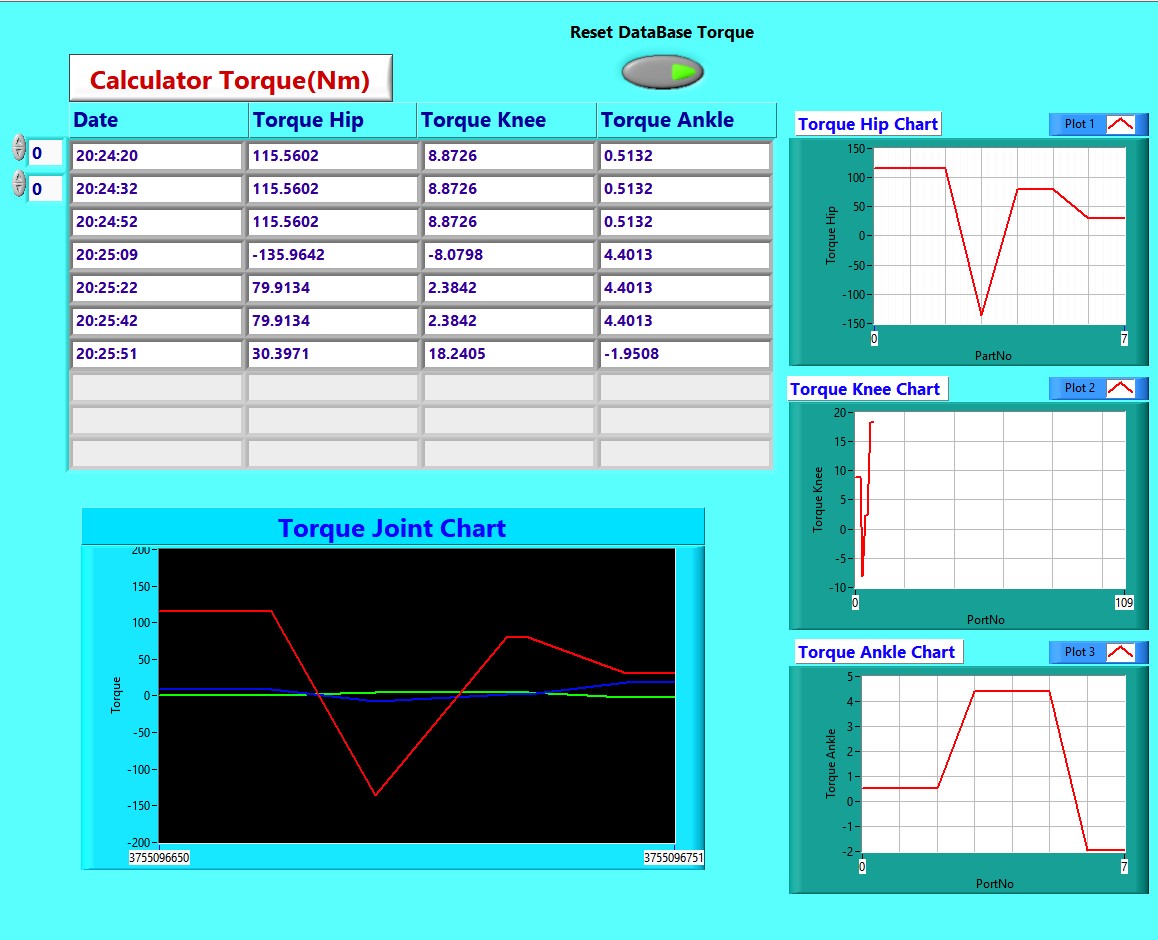
Table 8. Report Torque (Nm)
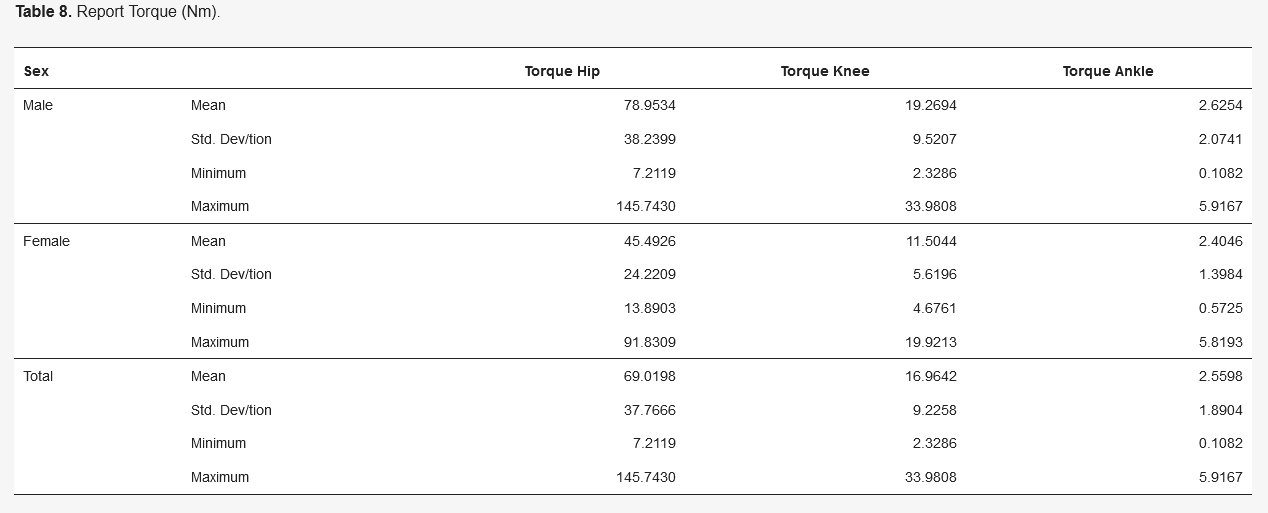
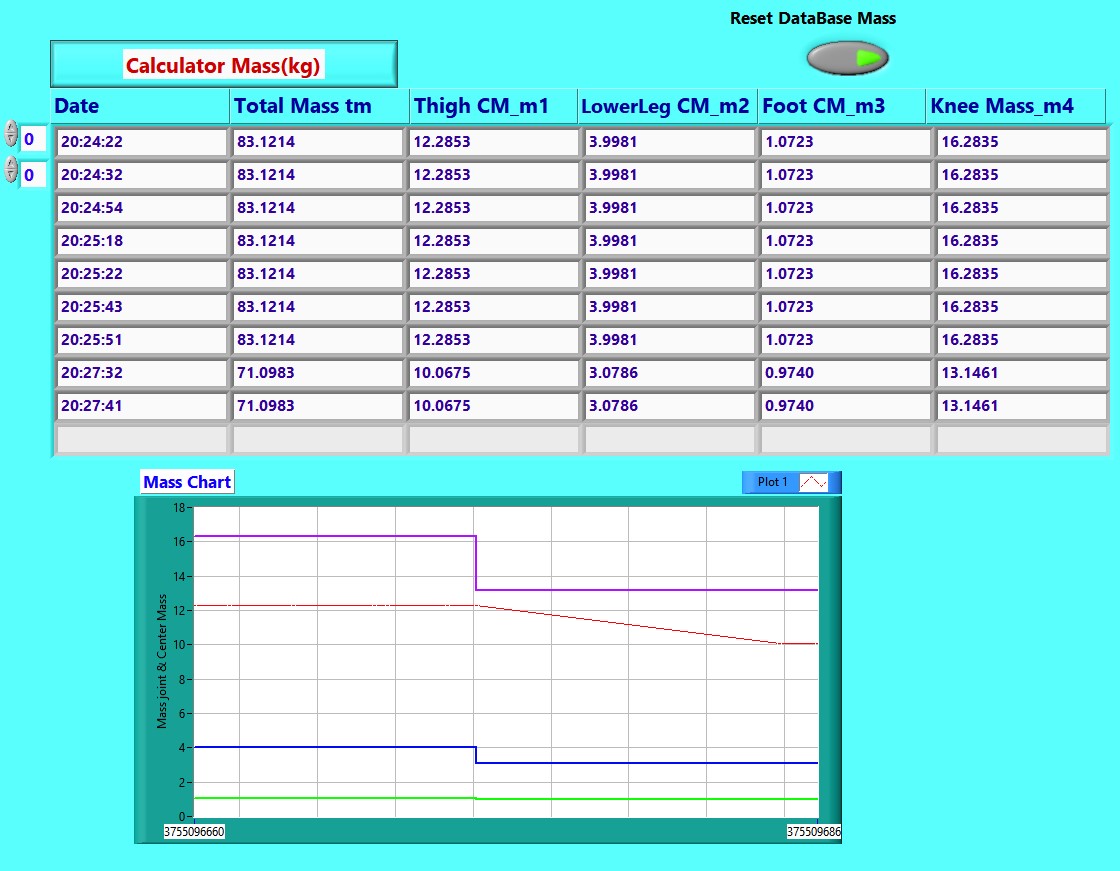
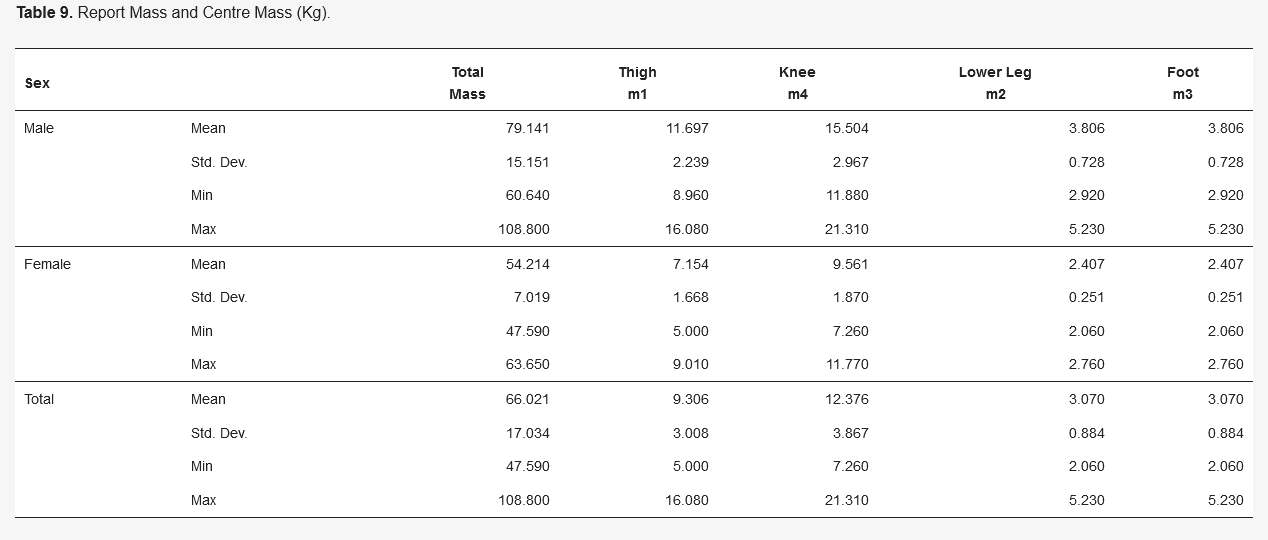
Table 9. Report Mass and Centre Mass (Kg)
FesRobex Torque Joints Calculation GUI